2.
The objective of each player is to place the opponent´s king "under
attack" in such a way that the opponent has no legal move which
would avoid the 'capture' of the king on the following move.
The player
who achieves this goal is said to have "checkmated" the opponent´s
king and to have won the game. The opponent whose king has been checkmated
has lost the game.
3.
If the position is such that neither player can possibly checkmate,
the game is drawn.
Laws
of Chess - The initial position of the pieces on the chessboard
1.
The chessboard is composed of an 8x8 grid of 64 equal squares alternately
light (the "white" squares) and dark (the "black"
squares).
The chessboard
is placed between the players in such a way that the near corner square
to the right of the player is white.
2.
At the beginning of the game one player has 16 light-coloured pieces
(the "white" pieces); the other has 16 dark-coloured pieces
(the "black" pieces):
These pieces
are as follows:
|
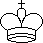
A
white king, usually indicated by the symbol
|
|
|
A
black king, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
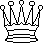
A
white queen, usually indicated by the symbol
|
|
|
A
black queen, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
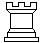
Two
white rooks, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
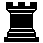
Two
black rooks, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
Two
white bishops, usually indicated by the symbol
|
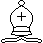 |
|
Two
black bishops, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
Two
white knights, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
Two
black knights, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
|
Eight
white pawns, usually indicated by the symbol
|
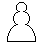 |
|
Eight
black pawns, usually indicated by the symbol
|
 |
3.
The initial position of the pieces on the chessboard is as follows:
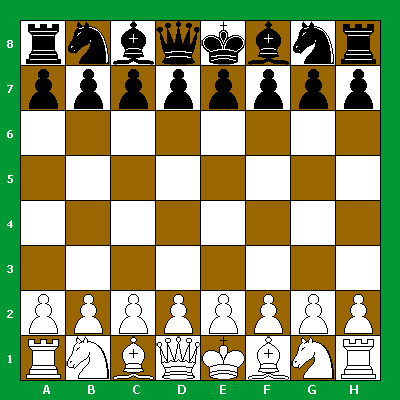
4.
The
eight vertical columns of squares are called "files". The
eight horizontal rows of squares are called "ranks". A straight
line of squares of the same colour, touching corner to corner, is called
a "diagonal".
